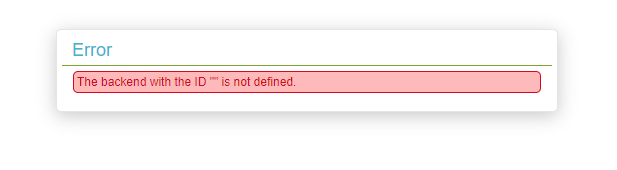
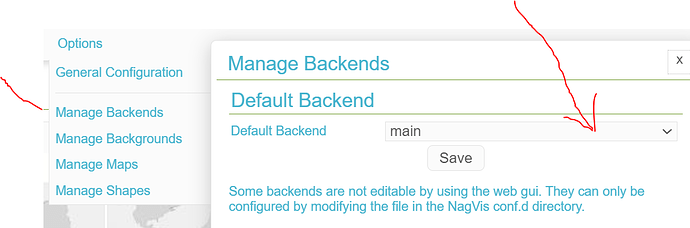
Thanks Andreas,
i added the nagvis.ini.php configuration. can you please check whether something is missing in there?
root@checkmk:/# find . -name nagvis.ini.php
./opt/omd/sites/production/.version_meta/skel/etc/nagvis/nagvis.ini.php
./opt/omd/sites/production/etc/nagvis/nagvis.ini.php
./opt/omd/versions/1.6.0p11.cre/skel/etc/nagvis/nagvis.ini.php
./opt/omd/versions/1.6.0p20.cre/skel/etc/nagvis/nagvis.ini.php
============================================================================
root@checkmk:/# cat /opt/omd/sites/production/etc/nagvis/nagvis.ini.php
; <?php return 1; ?>
; the line above is to prevent
; viewing this file from web.
; DON’T REMOVE IT!
; ----------------------------
; Default NagVis Configuration File
; At delivery everything here is commented out. The default values are set in the NagVis code.
; You can make your changes here, they’ll overwrite the default settings.
; ----------------------------
; ----------------------------
; !!! The sections/variables with a leading “;” won’t be recognised by NagVis (commented out) !!!
; ----------------------------
; General options which affect the whole NagVis installation
[global]
; Enable/Disable logging of security related user actions in Nagvis. For
; example user logins and logouts are logged in var/nagvis-audit.log
;audit_log=“0”
;
; Defines the authentication module to use. By default NagVis uses the built-in
; SQLite authentication module. On delivery there is no other authentication
; module available. It is possible to add own authentication modules for
; supporting other authorisation mechanisms. For details take a look at the
; documentation.
;authmodule=“CoreAuthModSQLite”
;
; Defines the authorisation module to use. By default NagVis uses the built-in
; SQLite authorisation module. On delivery there are some other modules available:
;
; - CoreAuthorisationModMySQL: Uses the same data structure as the SQLite authorisation
; module, but stores the data in a MySQL database.
; - CoreAuthorisationModMultisite: Uses information exported by Check_MKs Multisite
; to gather user permissions. This makes use of the roles defined for a user within
; multisite and the resulting permissions.
; - CoreAuthorisationModGroups: Assumes all users which should access NagVis are
; available in your monitoring core as contacts and assigned to contactgroups. Those
; contact group memberships are matched against a mapping table, which is defined in
; nagvis/etc/perms.db. This mapping table defines the permissions of each contact
; group within NagVis. Take a look at the docs for details.
;
; It is possible to add own authorisation modules for supporting other authorisation
; mechanisms. For details take a look at the documentation.
;authorisationmodule=“CoreAuthorisationModSQLite”
;
; If you use CoreAuthorisationModGroups above, you might need these options:
; This option defines the path to your group permission mapping table. This file
; is searched within the NagVis etc directory.
;authorisation_group_perms_file="/usr/local/nagvis/etc/perms.db"
; This option is used to configure one or several backend_ids, seperated by “,”, which
; should be used to get the users contact group memberships from.
;authorisation_group_backends=“live_1”
;
; Dateformat of the time/dates shown in nagvis (For valid format see PHP docs)
;dateformat=“Y-m-d H:i:s”
;
; Used to configure the preselected options in the “acknowledge problem” dialog
; dialog_ack_sticky=1
; dialog_ack_notify=1
; dialog_ack_persist=0
;
; File group and mode are applied to all files which are written by NagVis.
; Usualy these values can be left as they are. In some rare cases you might
; want to change these values to make the files writeable/readable by some other
; users in a group.
;file_group=""
;file_mode=“660”
;
; The server to use as source for the NagVis geomaps. Must implement the API which
; can be found on openstreetmap
;geomap_server=“geomap/”
;
; Public or private mirror of OpenStreetMap tiles server
;worldmap_tiles_url=“webseite check mk”
;worldmap_tiles_attribution=“© OpenStreetMap”
;
; Secondary “satellite” tiles server
;worldmap_satellite_tiles_url=""
;worldmap_satellite_tiles_attribution=""
;
; In some cases NagVis needs to open connections to the internet. The cases are:
; - The new geomap needs access to openstreetmap webservices to be able to fetch
; mapping information
; Most company networks don’t allow direct HTTP access to the internet. The most
; networks require the users to use proxy servers for outbound HTTP requests.
; The proxy url to be used in NagVis can be configured here. One possible value
; is “tcp://127.0.0.1:8080”.
;http_proxy=""
; Most proxies require authentication to access the internet. Use the format
; “:” to provide auth credentials
;http_proxy_auth=""
; Set the timeout (in seconds) for outbound HTTP requests (for example geomap requests)
;http_timeout=2
;
; Defines which translations of NagVis are available to the users
;language_available=“de_DE,en_US,es_ES,fr_FR,pt_BR,zh_CN”
; Language detection steps to use. Available:
; - User: The user selection
; - Session: Language saved in the session (Usually set after first setting an
; explicit language)
; - Browser: Detection by user agent information from the browser
; - Config: Use configured default language (See below)
;language_detection=“user,session,browser,config”
;
; Select language (Available by default: en_US, de_DE, fr_FR, pt_BR, zh_CN)
;language=“en_US”
;
; Defines the logon module to use. There are three logon modules to be used by
; default. It is possible to add own logon modules for serving other dialogs or
; ways of logging in. For details take a look at the documentation.
;
; The delivered modules are:
;
; LogonMixed: The mixed logon module uses the LogonEnv module as default and
; the LogonDialog module as fallback when LogonEnv returns no username. This
; should fit the requirements of most environments.
;
; LogonDialog: This is an HTML logon dialog for requesting authentication
; information from the user.
;
; LogonEnv: It is possible to realise a fully “trusted” authentication
; mechanism like all previous NagVis versions used it before. This way the user
; is not really authenticated with NagVis. NagVis trusts the provided username
; implicitly. NagVis uses the configured environment variable to identify the
; user. You can add several authentication mechanisms to your webserver,
; starting from the basic authentication used by Nagios (.htaccess) to single
; sign-on environments.
; Simply set logonmodule to “LogonEnv”, put the environment variable to use as
; username to the option logonenvvar and tell the authentication module to
; create users in the database when provided users does not exist. The option
; logonenvcreaterole tells the module to assign the new user to a specific role
; set to empty string to disable that behaviour.
;
; LogonMultisite: This module uses the authentication provided by auth_* cookies
; which have been generated by Check_MK multisite when using the cookie based
; authentication. Since 1.2.1i2 Check_MK uses a new cookie format. To be able
; to use this, you need to define a new option called logon_multisite_serials
; which points to the auth.serial file generated by Check_MK.
; Special options for this module:
;
; logon_multisite_htpasswd="/path/to/htpasswd"
; logon_multisite_serials="/path/to/auth.serials"
; logon_multisite_secret="/path/to/auth.secret"
; logon_multisite_createuser=“1”
; logon_multisite_createrole=“Guests”
;
;logonmodule=“LogonMixed”
;logonenvvar=“REMOTE_USER”
;logonenvcreateuser=“1”
;logonenvcreaterole=“Guests”
;
; Enable/Disable access to permitted monitoring objects only. This is useful if you want
; to restrict the access to status information by NagVis AND by the authorization mechanism
; of the monitoring software (e.g. Nagios).
;
; Disabled: access to status information is controlled by NagVis only. Every NagVis user who
; has access to a NagVis map can see the status of all objects on this map. If he has the
; permission to add objects to a map he can add ALL monitoring objects and is not restricted
; by the NagVis permission management.
;
; Enabled: every user in NagVis can see the status information only of those monitoring objects
; for which he has a contact definition in the monitoring software. This means that he
; can see status information only if he is allowed to access a map AND if he has the permission
; from the monitoring software for this object. The same applies to adding objects to a map.
;only_permitted_objects=0
;
; Default rotation time of pages in rotations
;refreshtime=60
;
; Some user information is stored in sessions which are identified by session
; cookies placed on the users computer. The options below set the properties
; of the session cookie.
; Domain to set the cookie for. By default NagVis tries to auto-detect this
; options value by using the webserver’s environment variables.
;sesscookiedomain=“auto-detect”
; Absolute web path to set the cookie for. This defaults to configured
; paths/htmlbase option
;sesscookiepath="/nagvis"
; Lifetime of the NagVis session cookie in seconds. The default value is set to
; 24 hours. The NagVis session cookie contents will be renewed on every page
; visit. If a session is idle for more time than configured here it will become
; invalid.
;sesscookieduration=“86400”
; Most modern browsers will deny javascript access to cookies if the HttpOnly
; flag is set. This prevents XSS attacks from stealing cookies. Default is off
; to not break any existing installations that rely on this functionality. Set
; to 1 to enable.
;sesscookiehttponly=0
; Most modern browsers will prevent cookies from being sent unencrypted if the
; Secure flag is set. Default is off since not all Nagvis installations require
; HTTPS. Set to 1 to enable.
;sesscookiesecure=0
;
; Staleness threshold (Only used with livestatus backend). Take a look at the
; Check_MK documentation for details about the staleness of hosts/services.
; The staleness means that an object has not received any state information for
; a given time. The configured value is a factor of the regular check interval.
; A value of 1.5 means that an object is marked as stale after one and a half
; check intervals have passed without update.
;staleness_threshold=1.5
;
; Start page to redirect the user to when first visiting NagVis without
; special parameters.
;startmodule=“Overview”
;startaction=“view”
; The startshow parameter is only used by some views at the moment. It is used
; by the Map module.
;startshow=""
;
; Turn on to enable some shinken related features in NagVis, like the
; min_business_impact-filter on automaps which can be used to render automaps
; based on the shinken attribute “business_impact”.
;shinken_features=0
; Path definitions
[paths]
; absolute physical NagVis path
;base="/usr/local/nagvis/"
; absolute html NagVis path
;htmlbase="/nagvis"
; absolute html NagVis cgi path
;htmlcgi="/nagios/cgi-bin"
; Default values which get inherited to the maps and its objects
[defaults]
; default backend (id of the default backend)
;backend=“live_1”
; background color of maps
;backgroundcolor="#ffffff"
; Enable/Disable the context menu on map objects. With the context menu you are
; able to bind commands or links to your map objects
;contextmenu=1
; Choose the default context template
;contexttemplate=“default”
; Raise frontend events for problematic objects also on page loading. Set to 1 to
; enable this feature
;event_on_load=0
; Repeat frontend events in the given interval. The interval is configured in seconds.
;event_repeat_interval=0
; The time in seconds to repeat alerts for a problematic ojects for as configured in
; event_repeat_interval. This value defaults to -1, this leads to repeated events
; till the problematic state has been fixed.
;event_repeat_duration=-1
; Enable/Disable changing background color on state changes (Configured color is
; shown when summary state is PENDING, OK or UP)
;eventbackground=0
; Enable/Disable highlighting of the state changing object by adding a flashing
; border
;eventhighlight=1
; The duration of the event highlight in milliseconds (10 seconds by default)
;eventhighlightduration=10000
; The interval of the event highlight in milliseconds (0.5 seconds by default)
;eventhighlightinterval=500
; Enable/Disable the eventlog in the new javascript frontend. The eventlog keeps
; track of important actions and information
;eventlog=0
; Loglevel of the eventlog (available: debug, info, warning, critical)
;eventloglevel=“info”
; Number of events kept in the scrollback
;eventlogevents=“24”
; Height of the eventlog when visible in px
;eventlogheight=“75”
; Hide/Show the eventlog on page load
;eventloghidden=“1”
; Enable/Disable scrolling to the icon which changed the state when the icon is
; out of the visible scope
;eventscroll=1
; Enable/Disable sound signals on state changes
;eventsound=1
; enable/disable header menu
;headermenu=“1”
; header template
;headertemplate=“default”
; Show states in the sidebar header menu (if supported by template)
;header_show_states=0
; enable/disable hover menu
;hovermenu=1
; hover template
;hovertemplate=“default”
; hover menu open delay (seconds)
;hoverdelay=0
; show children in hover menus
;hoverchildsshow=1
; limit shown child objects to n
;hoverchildslimit=“10”
; order method of children (desc: descending, asc: ascending)
;hoverchildsorder=“asc”
; sort method of children (s: state, a: alphabetical)
;hoverchildssort=“s”
; default icons
;icons=“std_medium”
; recognize only hard states (not soft)
;onlyhardstates=0
; recognize service states in host/hostgroup objects
;recognizeservices=1
; show map in lists (dropdowns, index page, …)
;showinlists=1
; show map in multisite snapin
;showinmultisite=1
; Name of the custom stylesheet to use on the maps (The file needs to be located
; in the share/nagvis/styles directory)
;stylesheet=""
; target for the icon links
;urltarget="_self"
; URL template for host object links
;hosturl="[htmlcgi]/status.cgi?host=[host_name]"
; URL template for hostgroup object links
;hostgroupurl="[htmlcgi]/status.cgi?hostgroup=[hostgroup_name]"
; URL template for service object links
;serviceurl="[htmlcgi]/extinfo.cgi?type=2&host=[host_name]&service=[service_description]"
; URL template for servicegroup object links
;servicegroupurl="[htmlcgi]/status.cgi?servicegroup=[servicegroup_name]&style=detail"
; URL template for dynamic group object links (disabled by default)
;dyngroupurl=""
; URL template for aggregations object links (disabled by default)
;aggrurl=""
; URL template for nested map links
;mapurl="[htmlbase]/index.php?mod=Map&act=view&show=[map_name]"
; URL template for host downtime link in context menus
;host_downtime_url="[html_cgi]/cmd.cgi?cmd_typ=55&host=[name]"
; URL template for host acknowledgement link in context menus
;host_ack_url="[html_cgi]/cmd.cgi?cmd_typ=96&host=[name]&force_check"
; URL template for service downtime in context menus
;service_downtime_url="[html_cgi]/cmd.cgi?cmd_typ=56&host=[name]&service=[service_description]"
; URL template for service acknowledgement in context menus
;service_ack_url="[html_cgi]/cmd.cgi?cmd_typ=7&host=[name]&service=[service_description]&force_check"
; Templates to be used for the different views.
;view_template=“default”
; Enable/disable object labels for all objects
;label_show=0
; Configure the colors used by weathermap lines
;line_weather_colors=“10:#8c00ff,25:#2020ff,40:#00c0ff,55:#00f000,70:#f0f000,85:#ffc000,100:#ff0000”
; Show mouse controllable elements for zooming the maps at the upper left corner of the map
;zoombar=0
; Enables scaling of the objects (icons, texts, lines, …) when zooming the map. This can be disabled
; to have the objects remain at the same size during zooming
;zoom_scale_objects=1
; Options to configure the Overview page of NagVis
backend=""
backgroundcolor="#8FE1FF"
[index]
; Color of the overview background
;backgroundcolor=#ffffff
; enable/disable header menu
;headermenu=“1”
; header template
;headertemplate=“default”
; Enable/Disable map listing
;showmaps=1
; Enable/Disable rotation listing
;showrotations=1
; Enable/Disable map thumbnails
;showmapthumbs=0
; Options for the Automap
[automap]
; Default URL parameters for links to the automap
;defaultparams="&childLayers=2"
; Default root host (NagVis uses this if it can’t detect it via backend)
; You can configure a hostname here or use “<<>>” as “virtual”
; node which shows the parent tree and all hosts which have no parents
; defined below the is node.
;defaultroot="<<>>"
; Path to the graphviz binaries (dot,neato,…); Only needed if not in ENV PATH
;graphvizpath="/usr/bin/"
; Options for the WUI
[wui]
; map lock time (minutes). When a user edits a map other users trying to edit
; the map are warned about this fact.
;maplocktime=5
; Show/hide the grid
;grid_show=0
; The color of the grid lines
;grid_color="#D5DCEF"
; The space between the single grid lines in pixels
;grid_steps=32
; Options for the new Javascript worker
[worker]
; The interval in seconds in which the worker will check for objects which need
; to be updated
;interval=10
; The retention time of the states in the frontend in seconds. The state
; information will be refreshed after this time
;updateobjectstates=30
; ----------------------------
; Backend definitions
; ----------------------------
; Example definition of a livestatus backend.
; In this case the backend_id is live_1
; The path /usr/local/nagios/var/rw has to exist
[backend_live_1]
backendtype=“mklivestatus”
; The status host can be used to prevent annoying timeouts when a backend is not
; reachable. This is only useful in multi backend setups.
;
; It works as follows: The assumption is that there is a “local” backend which
; monitors the host of the “remote” backend. When the remote backend host is
; reported as UP the backend is queried as normal.
; When the remote backend host is reported as “DOWN” or “UNREACHABLE” NagVis won’t
; try to connect to the backend anymore until the backend host gets available again.
;
; The statushost needs to be given in the following format:
; “<backend_id>:” → e.g. “live_2:nagios”
;statushost=""
;socket=“unix:/usr/local/nagios/var/rw/live”
; Example definition for a MySQL backend
; in this example the ID of the Backend is “ndomy_1” you can define another ID.
[backend_ndomy_1]
; type of backend - MUST be set
backendtype=“ndomy”
; The status host can be used to prevent annoying timeouts when a backend is not
; reachable. This is only useful in multi backend setups.
;
; It works as follows: The assumption is that there is a “local” backend which
; monitors the host of the “remote” backend. When the remote backend host is
; reported as UP the backend is queried as normal.
; When the remote backend host is reported as “DOWN” or “UNREACHABLE” NagVis won’t
; try to connect to the backend anymore until the backend host gets available again.
;
; The statushost needs to be given in the following format:
; “<backend_id>:” → e.g. “live_2:nagios”
;statushost=""
; hostname for NDO-db
;dbhost=“localhost”
; portname for NDO-db
;dbport=3306
; database name for NDO-db
;dbname=“nagios”
; username for NDO-db
;dbuser=“root”
; password for NDO-db
;dbpass=""
; prefix for tables in NDO-db
;dbprefix=“nagios_”
; instance name for tables in NDO-db
;dbinstancename=“default”
; maximum delay of the NDO Database in seconds
;maxtimewithoutupdate=180
; path to the cgi-bin of this backend
;htmlcgi="/nagios/cgi-bin"
; ----------------------------
; Rotation pool definitions
; ----------------------------
; in this example the browser switches between the maps demo and demo2 every 15
; seconds, the rotation is enabled by url: index.php?rotation=example
;[rotation_example]
; These steps are rotated. The single steps may have optional prefixes like “Demo2:”
; which are used as display text on the index pages rotation list.
; You may also add external URLs as steps. Simply enclose the url using []
; instead of the map name.
;maps=“map1,map2,map3”
; rotation interval (seconds)
;interval=15
; ----------------------------
; Action definitions
; ----------------------------
; Since NagVis 1.7.6 it is possible to use so called actions to extend the
; default context menu. This enables users to connect directly to the monitored
; hosts from the NagVis context menu. Here you can configure those actions.
;
; It is possible to add such actions to the context menus of service and host
; objects. They are not added blindly to all objects of those types, you can
; use the attribute “condition” to configure which objects shal have the
; specific actions. By default we use Nagios custom macros of the host object
; to make the actions visible/invisible. This filtering mechanism is not limited
; to custom macros, you can also use regular host attributes which are available
; within NagVis.
; With the option “client_os” you can configure the option to only be available
; on the clients which have a listed operating system running.
; Adds the action “connect via rdp” to service/host objects where the host object
; has the string “win” in the TAGS Nagios custom macro.
; When clicking on the link, NagVis generates a .rdp file which contains makes
; the client connect to the given host via RDP.
;[action_rdp]
;action_type=“rdp”
;obj_type=“host,service”
;condition=“TAGS~win”
;client_os=“win”
;domain=""
;username=""
; Adds the action “connect via ssh” to service/host objects which have the
; string “unix” in the TAGS Nagios custom macro. Is only added when NagVis
; detects that the client watching the map uses windows.
; When clicking on the link, NagVis generates a .cmd file which contains a
; call to putty which makes putty connect via SSH to this host.
;[action_win_ssh]
;action_type=“win_ssh”
;obj_type=“host,service”
;client_os=“win”
;condition=“TAGS~unix”
; Adds the action “connect via ssh” to service/host objects which have the
; string “unix” in the TAGS Nagios custom macro. Is only added when NagVis
; detects that the client watching the map uses linux or mac os.
; When clicking on the link, the browser opens the URL ssh:///,
; you need to configure your clients browser to handle these urls correctly.
;[action_ssh_url]
;action_type=“ssh_url”
;obj_type=“host,service”
;client_os=“mac,lnx”
;condition=“TAGS~unix”
; Adds the action “connect via http” to service/host objects which have the
; string “web-80” in the TAGS Nagios custom macro
; When clicking on the link, the browser opens a new window with the URL
; http://<host_address>/. This can be changed by modyfing the context template.
;[action_http]
;action_type=“http”
;obj_type=“host,service”
;condition=“TAGS~web-80”
; Adds the action “connect via http” to service/host objects which have the
; string “web-443” in the TAGS Nagios custom macro
; When clicking on the link, the browser opens a new window with the URL
; https://<host_address>/. This can be changed by modyfing the context template.
;[action_https]
;action_type=“https”
;obj_type=“host,service”
;condition=“TAGS~web-443”
; ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
; Below you find some advanced stuff
; ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
; Configure different state related settings
[states]
; State coverage/weight: This defines the state handling behaviour. For example
; a critical state will cover a warning state and an acknowledged critical
; state will not cover a warning state.
;
; These options are being used when calculating the summary state of the map
; objects. The default values should fit most needs.
;
;down=10
;down_ack=6
;down_downtime=6
;unreachable=9
;unreachable_ack=6
;unreachable_downtime=6
;critical=8
;critical_ack=6
;critical_downtime=6
;warning=7
;warning_ack=5
;warning_downtime=5
;unknown=4
;unknown_ack=3
;unknown_downtime=3
;error=4
;error_ack=3
;error_downtime=3
;up=2
;ok=1
;unchecked=0
;pending=0
;
; Colors of the different states. The colors are used in lines and hover menus
; and for example in the frontend highlight and background event handler
;
;unreachable_bgcolor=#F1811B
;unreachable_color=#F1811B
;unreachable_ack_bgcolor=
;unreachable_downtime_bgcolor=
;down_bgcolor=#FF0000
;down_color=#FF0000
;down_ack_bgcolor=
;down_downtime_bgcolor=
;critical_bgcolor=#FF0000
;critical_color=#FF0000
;critical_ack_bgcolor=
;critical_downtime_bgcolor=
;warning_bgcolor=#FFFF00
;warning_color=#FFFF00
;warning_ack_bgcolor=
;warning_downtime_bgcolor=
;unknown_bgcolor=#FFCC66
;unknown_color=#FFCC66
;unknown_ack_bgcolor=
;unknown_downtime_bgcolor=
;error_bgcolor=#0000FF
;error_color=#0000FF
;up_bgcolor=#00FF00
;up_color=#00FF00
;ok_bgcolor=#00FF00
;ok_color=#00FF00
;unchecked_bgcolor=#C0C0C0
;unchecked_color=#C0C0C0
;pending_bgcolor=#C0C0C0
;pending_color=#C0C0C0
;
; Sound of the different states to be used by the sound eventhandler in the
; frontend. The sounds are only being fired when changing to some
; worse state.
;
;unreachable_sound=std_unreachable.mp3
;down_sound=std_down.mp3
;critical_sound=std_critical.mp3
;warning_sound=std_warning.mp3
;unknown_sound=
;error_sound=
;up_sound=
;ok_sound=
;unchecked_sound=
;pending_sound=
; -------------------------
; EOF
; -------------------------